Available 6 days a week at MUMS Solihull
£85
Average rating: 4.87 / 5 Read all reviews
| Early Pregnancy Scan up to 12 weeks | £85 | |
| Early Pregnancy Scan and Consultation with a Gynaecologist | £150 |
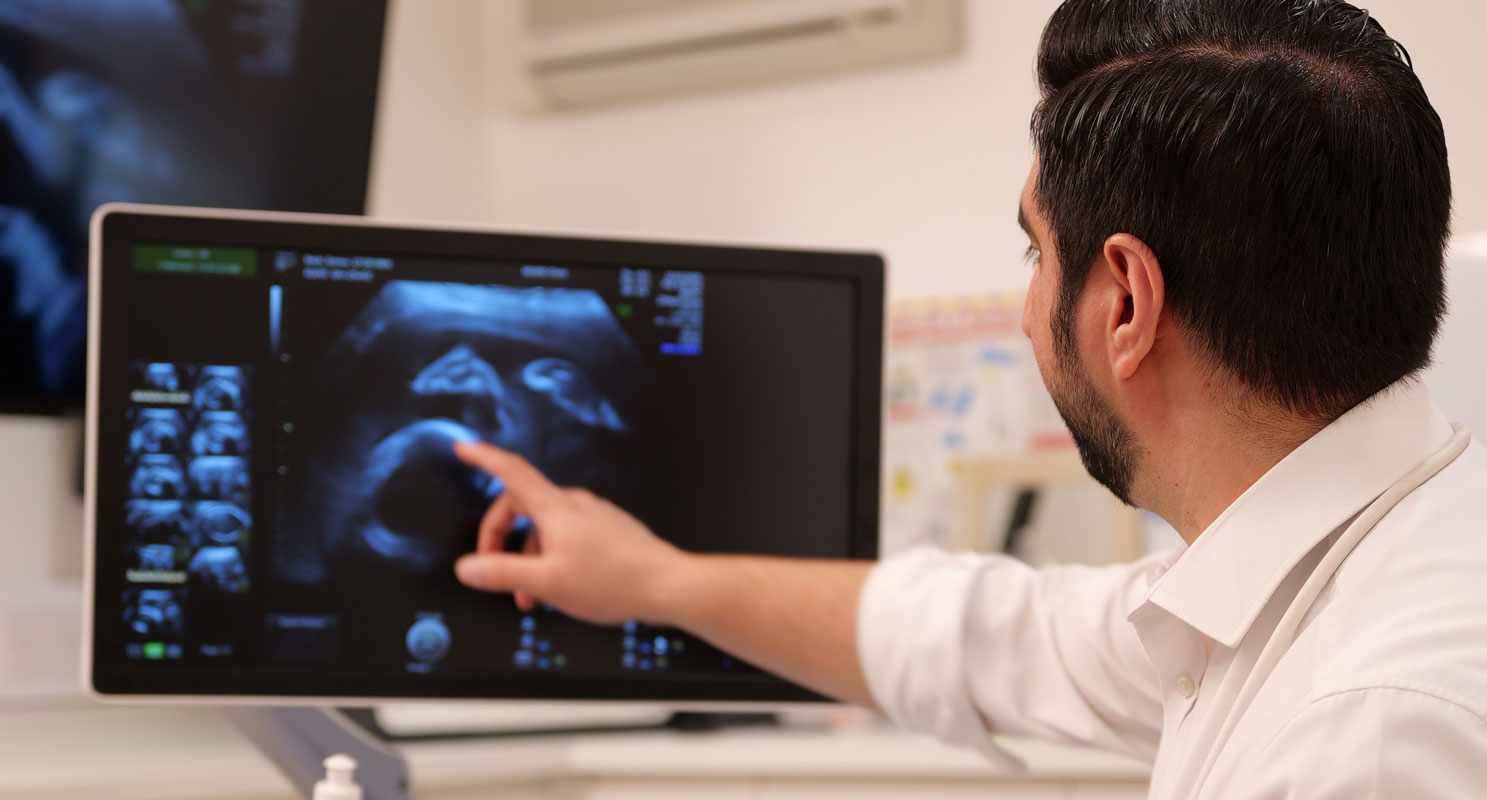
At MUMS we specialise in Early Pregnancy/Dating Scans 6 days a week including Saturdays. All our sonographers, Gynaecologists, and Fetal Medicine consultants are highly skilled and trained to perform both transabdominal (TA) and transvaginal (TV) ultrasound scans. Our Sonographers are Vicky Parsons, Bubby Bhandal, and Helen Grant – all of which have huge experience in the NHS and privately. They are qualified to perform diagnostic early pregnancy scans. Our consultants are Miss Poonam Pradhan – Consultant Gynaecologist, Miss Natalie Woodhead – Consultant Gynaecologist, Mr Anoop Rehal, Consultant in Fetal Medicine, and Mr Davide Casagrandi, Speciality Doctor in Obstetrics and Gynaecology. MUMS Consultants are highly qualified specialists with NHS and Private experience in diagnostic pregnancy scanning. Doctors in obstetrics and gynaecology (O&G) care for pregnant women and unborn babies and look after women’s sexual and reproductive health.
Early pregnancy scans cost £85.
Early Pregnancy scans with a Consultant Gynaecologist, including a consultation, when specialist care is required cost £150
Early pregnancy scans are sometimes referred to as viability scans or early dating scans – provide reassurance at the early pregnancy stage up to 12 weeks. If you are beyond 12 weeks and up to 16 weeks, then you will need a Reassurance Scan. We offer 16-20 week fetal development scans and so if you are 16 weeks or over then click here for more information.
We can perform your early pregnancy scan as early as 6 weeks, although we recommend being at least 6 weeks and 4 days to ensure that a heartbeat can be seen. You can calculate this from the 1st day of your last menstrual period. If you are unsure of your dates or have irregular cycles, we recommend you are scanned two weeks after your first positive pregnancy test. We offer Beta HCG pregnancy blood testing. We often suggest this test where the early pregnancy scan does not detect a pregnancy because it is too early to scan
The NHS do not routinely offer early pregnancy scans and lots of women chose a private early pregnancy scan. The scan can confirm the pregnancy is in the correct place (uterus), confirm a heartbeat, confirm whether there are one or more babies and date the pregnancy.
Early pregnancy scans can be performed to confirm the results of a pregnancy test and provide reassurance that everything is progressing normally.
Our professional clinicians are caring and ensure you receive excellent care and advice and the appropriate support you need.
We can perform an early pregnancy scan just after 5 weeks (to look at the location of the pregnancy sac). This will give reassurance that the pregnancy is developing in the womb and not in the fallopian tubes ( ectopic pregnancy ). This scan will be performed transvaginally. At this early stage we will not see a heartbeat.
If the reason for the scan is pain or bleeding – we are more than happy to scan you. Our clinic is renowned for its friendly, sympathetic staff who will explain in detail the scan findings, offer you blood tests such as Beta HCG ( Advanced Pregnancy Test ), follow up scans and the appropriate pathway, where indicated.
Knowing that the pregnancy is developing normally can alleviate various concerns at an anxious time.
We normally perform early pregnancy scans trans-abdominally (via your tummy). However – we may have to scan you internally (transvaginally) for early gestations (6-7 weeks) to obtain clearer images. There are several reasons for this. If your womb tilts backwards (retroverted) or you are less pregnant that your calculations.
Ultrasound scans are safe. They cause no discomfort. We use single use ultrasound gel on the abdomen. The ultrasound probe presses on your tummy which transmits images on our screens. If your bladder is too full it can be a little uncomfortable but should not be painful.
The scan usually takes around 5-10 minutes from start to finish. If the images are unclear, you will be offered a transvaginal ultrasound scan ( internal). We explain the findings to you throughout and at the end of the scan.
Following your scan, we will give you your detailed report and you will have the opportunity to ask any questions. Your scan will then be uploaded along with your images onto a USB memory stick to take home on the day.
6 weeks
We can see the gestation sac with a fetal pole developing in your uterus at this early stage. Additionally, we should see and hear the baby’s heartbeat. This is reassuring. However, if we are unable to see this then you could be too early for an ultrasound scan, or it might be that the pregnancy is not viable.
7 weeks
At 7 weeks we can see a fetal heartbeat. We can see the embryo and measure from the baby’s head to its bottom and calculate how far pregnant you are. We call this a dating scan. Miscarriage risk is reduced to about 5% if the heartbeat is present at this stage.
8 weeks
At 8 weeks we can see the baby making movements. This is very reassuring, and we can calculate the gestation of the pregnancy. Miscarriage risk is reduced to 2% if the heartbeat is present at this stage.
9-10 weeks
At 9 weeks we can see the baby developing and assess the growth and the risk of miscarriage is reduced to 1% where the heartbeat is seen and heard at this stage.
You can book online, call us on 0121 704 2669 or request a scan online. If you decide to book online, please ensure you are at least 6 weeks to avoid having to be re-scanned when views of the heartbeat are visible and heard.
We have ample parking and great reviews.
If you are over 12 weeks there is no need to attend with a full bladder.
Copyright © 2026 Midland Ultrasound and Medical Services | Company number: 04844920